Major update: 17th January 2022
Did all humanity come from Noah’s three sons?
The Bible says ‘yes’ and is known as the ‘Table of Nations’ and we learn how humanity increased and from the middle east, they eventually spread out over the whole world.
Archaeology tells us that all of humanity spread out at a certain point in time from the middle east.
Modern genetics tells us that the whole of humanity can be traced back to one woman in the middle east.
The Bible explains how we can trace back the world’s population to three genetic haplogroups.
Table of Contents menu:
Table of Contents:
1. Were there any of Noah’s relatives around at the time of the Flood?

Noah and his wife, and his three sons and their wives went onto the Ark, but were there any other close family relatives alive then?
The Bible has a detailed family tree giving the ages of each person and the age they had each child.
From that information I created this diagram to scale:
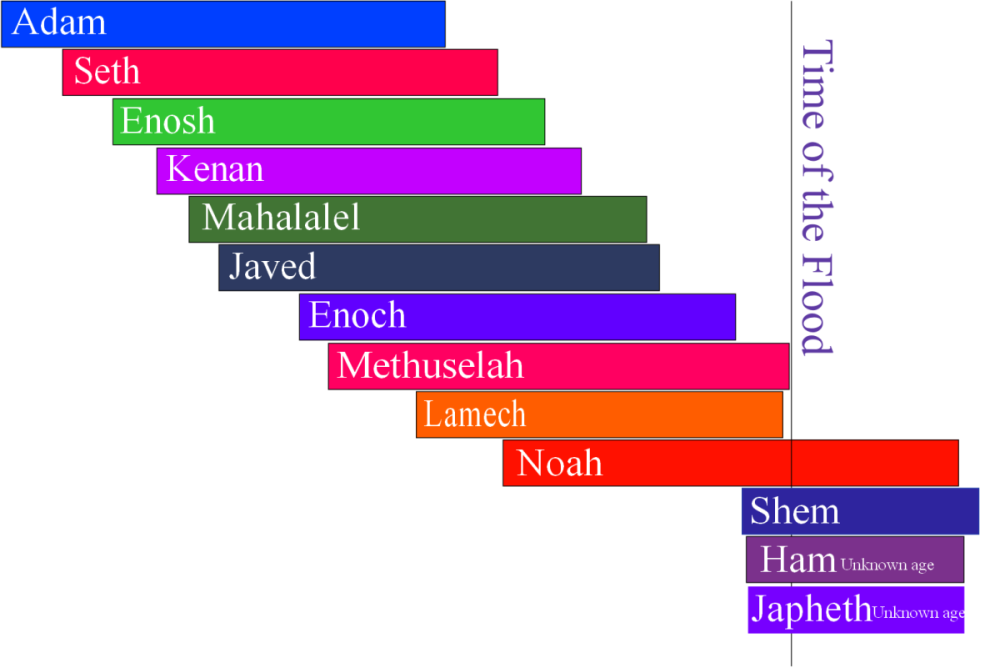
To use this image please quote notmanywise.uk thanks. By Peter Reason licensed under CC BY-SA 2.0.
This information is found in Genesis 5:25-32 and it just follows the direct line of sons from Adam to Noah’s son Shem.
Cain was Adam and Eve’s first born son and Abel followed, but unfortunately Cain killed Abel and Abel was childless.
Seth was a replacement for Abel:
Adam made love to his wife again, and she gave birth to a son and named him Seth, saying,
Genesis 4:25 NIV
‘God has granted me another child in place of Abel since Cain killed him.’ ”
Why is childbirth so painful for humans, if evolution was true, surely humans would have evolved to painless childbirth.
Also, how can sexual reproduction start and evolve over time? Scientists have no answer to this dilemma.
Cain did have children but we are not told their ages or when they had children.
All the names on my graph had other sons and daughters but again there is not enough information to be able to add them to it.
On the graph, all the timelines are to scale and when their son was born is also all to scale.
Also, the vertical line represents when the flood came and you can see that all of Adam’s chosen line died BEFORE the flood came apart from one; Noah along with his wife, his three sons and their wives.
- Noah’s father, Lamech, died five years before the flood and
- Noah’s grandfather, Methuselah, died in the same year as the flood.
The flood was worldwide and was a horrendous extermination.
Could Noah have built the Ark? Many ancient peoples were skilled craftsmen.
2. The Generations of Noah or Table of Nations
Noah’s three sons Shem, Ham and Japheth, from which 18th century German scholars at the Göttingen School of History derived the race terminology Semites, Hamites and Japhetites.
‘Generations of Noah’ Wikipedia 1
Certain of Noah’s grandsons were also used for names of peoples: from Elam, Ashur, Aram, Cush, and Canaan were derived respectively:
the Elamites, Assyrians, Arameans, Cushites, and Canaanites.
Likewise, from the sons of Canaan: Heth, Jebus, and Amorus were derived:
Hittites, Jebusites, and Amorites.
Further descendants of Noah include Eber – from Shem (from whom come the ‘Hebrews’);
the hunter-king Nimrod – from Cush;
and the Philistines – from Misrayim.”
The list of 70 names from Noah’s relatives recorded in Genesis, the Table of Nations, tells us of the spread of peoples at a certain time in history.
Opponents to the factualness of Noah’s offspring say that the spread of people doesn’t account for native American Indians, Aborigines, etc.
But I would say after this particular time in history that the Bible is describing here, people probably kept travelling and dispersing throughout the world and they would eventually get to, and populate the distant lands.
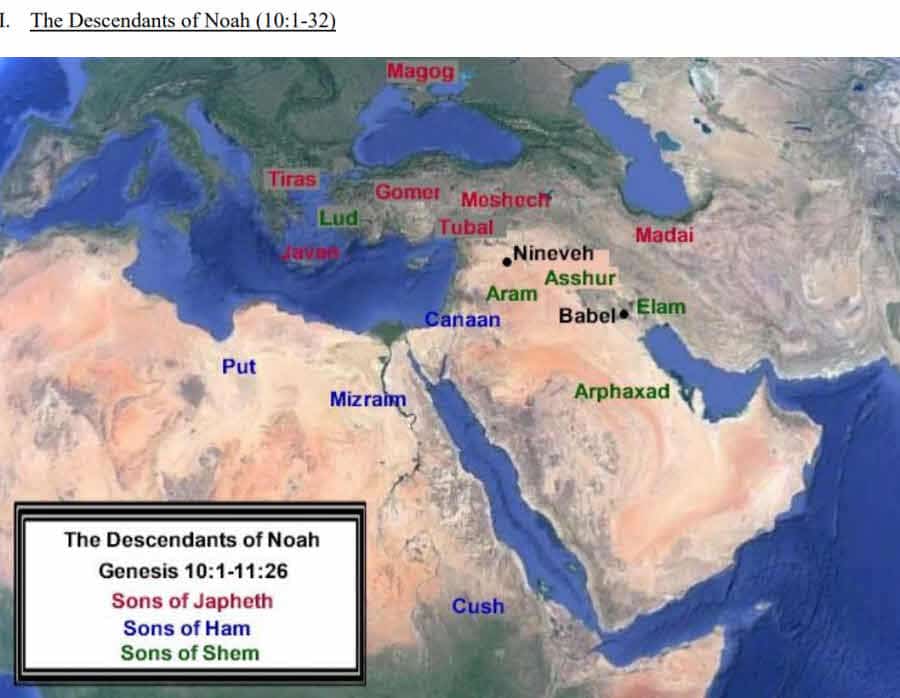
There was an attempt to classify these family groups and to divide humankind into three races called Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid (originally named ‘Ethiopian’), terms which were introduced in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen School of History.
‘Generations of Noah’ Wikipedia
It was obviously wrong, but understandable, to try and classify mankind based on visual features; ‘Caucasoid, Mongoloid, and Negroid’.
So is there any other way of classifying the human race?
3. Human groups according to modern genetics
Scientists are now categorising mankind by studying DNA.
Is there any chance that there would be three groups which correspond to the three sons of Noah?
Well, the mitochondrial haplogroups are divided into three main groups, which are designated by the sequential letters L, M, and N.
Shortly after the migration, the large R group split off from the N. 3
Modern genetics tells us that there was a central dispersal from Africa by three main mitochondrial lineages, with people travelling in small groups into areas where no humans had ever been.
That sounds extraordinarily close to the Biblical explanation, except the timings are very different.
Also tantalisingly, there is a woman at the root of all these groups, for all humans currently living, who is commonly called Mitochondrial Eve.
The majority of scientists would say that the universe started billions of years ago, but a number of scientists believe in the creation account in Genesis.
That does not mean that the majority of scientists accept the Big Bang theory. See the article: Evidence for the Big Bang.
So evolution based on modern genetics says that:
- all currently living humans came from Mitochondrial Eve
- that there was a serious genetic bottleneck
- there was a single dispersal of people around the world.
The Bible says, and agrees with modern genetics, on these points:
- entire human race came from Eve (and Adam!)
- a world-wide flood caused a serious population crash
- at the Tower of Babel there was a single dispersal of people across the world.
a) Are haplogroups different people groups of the world?
Yes, haplogroups eventually form the world’s different groups that we see now.
The different groups of humanity are called haplogroups, which have been given letters from the alphabet.
Groups such as those from Africa, Somalia, Siberia, East Asia, Mongolians, Central Asians, Koreans, etc.
What are haplogroups?
‘What are Haplogroups?’ Living DNA 4
According to the International Society of Genetic Genealogy, a haplogroup is a genetic population group of people who share a common ancestor on either their paternal or maternal line.
Particular haplogroups are associated with well-known ancestral groups such as the Vikings, Aboriginal Australians, and the Celts…
Haplogroups follow male and female descendancy lines, with Y-DNA passing from father to son, and mtDNA passing from mothers to both daughters and sons.
All haplogroups started as the original haplogroup in Africa, and as the many millennia have passed by, more and more haplogroups have come to be.
Each time the DNA has mutated, a group has split off and they have become their own haplogroup.”
b) What are maternal haplogroups?
By reading the quote above you may have realised that there are two types of haplogroups – one following the male side and the other the female side:
Maternal haplogroups (from the mother) are determined by assessing mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
‘What are Haplogroups?’ Living DNA
Unlike other types of DNA, the mtDNA is found outside the cell nucleus and that means it does not mix with other types of DNA.
This also means that you will have the same maternal haplogroup as everyone else in your direct maternal line:
your mum, brother, sister, aunt, and grandmother on your mother’s side.
Follow that haplogroup back to its origins and you’ll find a single mutation occurred at some point in history.”
And some more info on the maternal haplogroups:
Understanding the evolutionary path of the female lineage has helped population geneticists trace the matrilineal inheritance of modern humans back to human origins in Africa and the subsequent spread across the globe.
‘Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup’ International Society of Genetic Genealogy Wiki 5
The letter names of the haplogroups run from A to Z.
As haplogroups were named in the order of their discovery, they do not reflect the actual genetic relationships.
The woman at the root of all these groups is the matrilineal most recent common ancestor (MRCA) for all currently living humans.
She is commonly called Mitochondrial Eve.”
c) What is a paternal haplogroup?
The paternal haplogroup relates to your Y chromosome, and since that is the sex-determining chromosome for men, it is passed down from father to son.
‘What are Haplogroups?’ Living DNA 6
As women don’t have a Y chromosome, they will not have a paternal haplogroup by default, however, they are able to find out what their paternal haplogroup is if a male relative from the father’s side (ideally a brother, father, uncle, or grandfather) is also tested.”
4. What Mitochondrial DNA could have been on Noah’s Ark?
So how many people groups were on Noah’s Ark?
As far as the Bible is concerned, we could say three because three people groups spread throughout the Earth.
From the Ark the people did not initially spread out, they disobeyed God and they travelled to Babel increasing in number as they went.
From there, God scattered them and they went out from Babel.
So, genetically how many groups were on the Ark?
How many mitochondrial DNA lineages were on the Ark?
‘Adam, Eve and Noah vs Modern Genetics’ by Dr Robert W. Carter 7
The answer: three (the 3 wives of Noah’s sons)…
Your genome is like an encyclopedia (almost literally).
And, like an encyclopedia, the genome is broken down into volumes, called chromosomes, but you have two copies of each volume (with the exception of the X and Y chromosomes; women have two Xs but men have one X and one Y)…
How many X chromosome lineages were on the Ark?
That depends.
If you count it all up, you get eight.
If, by chance, Noah’s wife passed on the same X chromosome to each of her three sons (25% probability), then there were seven.
If Noah had a daughter after the Flood (not expected, but possible), there could be as many as nine X chromosome lineages.
Either way, this is a considerable amount of genetic material. And since X chromosomes recombine (in females), we are potentially looking at a huge amount of genetic diversity within the X chromosomes of the world.
Does this fit the evidence? Absolutely!
It turns out that Y chromosomes are similar worldwide. According to the evolutionists, no ‘ancient’ (i.e., highly mutated or highly divergent) Y chromosomes have been found.
This serves as a bit of a puzzle to the evolutionist, and they have had to resort to calling for a higher ‘reproductive variance’ among men than women, high rates of ‘gene conversion’ in the Y chromosome, or perhaps a ‘selective sweep’ that wiped out the other male lines.
For the biblical model, it is a beautiful correlation and we can take it as is.”
Is science beginning to make us lose our faith?
We are told that there is so much evidence for evolution, like anatomy proves change, molecular homology, biogeography, and fossils, but do they really?
Are dragons based on real dinosaur-type creatures?
5. What are the three genetic groups of the world?
Here we look at the three main types of Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) lineages in detail:
The mitochondrial haplogroups are divided into three main groups, which are designated by the sequential letters L, M, N.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia 8
Humanity first split within the L group between L0 and L1-6. L1-6 gave rise to other L groups, one of which, L3, split into the M and N group.”
a) The L-type Haplogroup – mainly Africans
The L type consists of nearly all Africans.
The map below shows the distribution of the Mitochondrial DNA Haplogroup types throughout the world.
It starts in Africa with L type and branches out with M and N types.
Quickly the R type branches out from N.
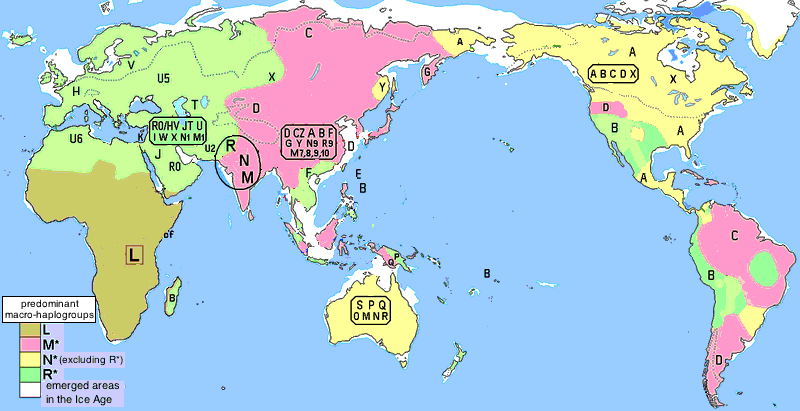
b) The M type Haplogroup – travelled east
The M group comprises the first wave of human migration which is thought to have evolved outside of Africa, following an eastward route along southern coastal areas.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia
Descendant lineages of haplogroup M are now found throughout Asia, the Americas, and Melanesia, as well as in parts of the Horn of Africa and North Africa; almost none have been found in Europe.
The M type consists of:
- Ethiopian, Somali and Indian populations.
- Many Siberians, some Amerindian, many Saami, some Korean, some North Chinese, some Central Asian populations.
- Some Amerindians, many Siberians and northern East Asians
- Malay, Borneo, Philippines, Taiwanese aborigines, Papua New Guinea
- Many N. E. Siberians, northern East Asians, and Central Asians
- Melanesian, Polynesian, New Guinean populations
c) The N Haplogroup – travelled north
The N haplogroup may represent another macrolineage that evolved outside of Africa, heading northward instead of eastward.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia
Shortly after the migration, the large R group split off from the N.”
The N type consists of:
- Many Amerindians and some East Asians and Siberians
- Few in Northern, Eastern Europe
- Some Australian aborigines
- Some Eastern Europeans, South and S.E. Asians
- Some Amerindians, Southern Siberians, S. W. Asians, and Southern Europeans
- Most Nivkhs and people of Nias; many Ainus, Tungusic people, and Austronesians; also a few in Siberia, East and Central Asia
d) The next main Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) in detail:
Haplogroup R consists of two subgroups defined on the basis of their geographical distributions, one found in south-eastern Asia and Oceania and the other containing almost all of the modern European populations.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia
Haplogroup N(xR), i.e. mtDNA that belongs to the N group but not to its R subgroup, is typical of Australian aboriginal populations, while also being present at low frequencies among many populations of Eurasia and the Americas.”
R – Large group found within the N type – travelled to Europe and Asia
Populations contained therein can be divided geographically into West Eurasia and East Eurasia.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia
Almost all European populations and a large number of Middle-Eastern population today are contained within this branch.
A smaller percentage is contained in other N type groups (See above).
Below are subclades of R:
- Some Chinese, Tibetans, Mongolians, Central Asians, Koreans, Amerindians, South Siberians, Japanese, Austronesians
- Mainly found in S.E. Asia, Hvar Island in Croatia.
- Found in Arabia and among Ethiopians and Somalis; Europe, Western Asia, North Africa;
- Lebanon area, some Bedouin populations, North, Eastern Europe, Indus, Mediterranean
- Many in West Eurasia, Indian sub-continent, and Algeria and rest of Europe.
‘Haplogroup’ Wikipedia.
There seems enough evidence from modern science to support the Bible’s Table of Nations – the spread of mankind from the Ark to eventually getting to every corner of the globe.
Some of the Scientific community question the Big Bang’s validity, whilst others seem to want to grasp any answer except the one that points towards a Creator.
Are scientists always right?
Most scientists trust in unchanging mathematical and scientific laws without questioning why they are there.
Horse evolution used to ‘prove’ evolution, but it actually doesn’t…
6. Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Who were Noah’s siblings?
The Bible does not tell us how many siblings Noah had or what were their names.
We are only told that Lamech (Noah’s father): fathered Noah and then “had other sons and daughters.”
An interesting fact is that when Noah was born his father said: “Out of the ground that the Lord has cursed, this one shall bring us relief from our work and from the painful toil of our hands.”
Who is related to Noah?
We are all related to Noah – everyone on the planet.
But Noah’s nearest relatives were:
Noah’s great grandad: Enoch.
(Great grandmother: unknown).
Noah’s grandad: Methuselah.
(Grandmother: unknown).
(Noah’s uncle and aunts: unknown).
Noah’s father: Lamech.
(Noah’s mother: unknown).
(Noah’s wife: unknown).
Noah’s children: Shem, Ham and Japheth. (Their wives: unknown).
Noah’s grandchildren: Shem
Noah’s great-grandchildren:
(From Shem): Elam, Asshur, Arpachshad, Lud and Aram.
(From Ham): Cush, Egypt, Put, and Canaan.
(From Japheth): Gomer, Magog, Madai, Javan, Tubal, Meshech and Tiras.
What was Noah wife name?
The Bible does not give the name of Noah’s wife.
There are some ancient speculative theories:
1) Noah’s wife may have been: Naamah the sister of Tubal-Cain from the male line that runs back to Cain – the son of Adam and Eve.
This comes from ‘The Bereshith’ or ‘Genesis Rabba’, a selection of sayings from the work translated into English by Samuel Rapaport.
2) Noah’s wife may have been a different Naamah, a daughter of Enoch from the male line that runs back to Seth (Adam and Eve’s third son to replace the loss of Abel).
This comes from the ‘Book of Jasher’ a medieval Jewish midrash, translated by Samuel Moses. (Parry, J. H. ed.)
How many wives did Noah have on the ark?
Noah had one wife.
But if we are asking how many ladies were on Noah’s Ark that could produce children, then there were three.
The three wives of Noah’s sons would have children after they came off the Ark.
Noah’s wife is not recorded as having any more children.
References open in new tabs:
‘Mitochondrial DNA haplogroup’ International Society of Genetic Genealogy Wiki ↩
‘Adam, Eve and Noah vs Modern Genetics’ by Dr Robert W. Carter Creation.com ↩
User:Maulucioni, CC BY-SA 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons ↩

